- Research Article
- Open access
- Published:
Fuzzy Stability of an Additive-Quadratic-Quartic Functional Equation
Journal of Inequalities and Applications volume 2010, Article number: 253040 (2010)
Abstract
Using the fixed point method, we prove the generalized Hyers-Ulam stability of the following additive-quadratic-quartic functional equation: 










 in fuzzy Banach spaces.
in fuzzy Banach spaces.
1. Introduction and Preliminaries
Katsaras [1] defined a fuzzy norm on a vector space to construct a fuzzy vector topological structure on the space. Some mathematicians have defined fuzzy norms on a vector space from various points of view [2–4]. In particular, Bag and Samanta [5], following Cheng and Mordeson [6], gave an idea of fuzzy norm in such a manner that the corresponding fuzzy metric is of Kramosil and Michálek type [7]. They established a decomposition theorem of a fuzzy norm into a family of crisp norms and investigated some properties of fuzzy normed spaces [8].
We use the definition of fuzzy normed spaces given in [5, 9, 10] to investigate a fuzzy version of the generalized Hyers-Ulam stability forthe following functional equation

in the fuzzy normed vector space setting.
Definition 1.1 (see [5, 9–11]).
Let  be a real vector space. A function
be a real vector space. A function 
 is called a fuzzy norm on
is called a fuzzy norm on  if for all
if for all  and all
and all  ,
,
 for
for  ;
;
 if and only if
if and only if  for all
for all  ;
;
 if
if  ;
;
 ;
;
 is a nondecreasing function of
is a nondecreasing function of  and
and  ;
;
for  ,
,  is continuous on
is continuous on  .
.
The pair  is called a fuzzy normed vector space.
is called a fuzzy normed vector space.
The properties of fuzzy normed vector spaces and examples of fuzzy norms are given in [9, 12].
Definition 1.2 (see [5, 9–11]).
Let  be a fuzzy normed vector space. A sequence
be a fuzzy normed vector space. A sequence  in
in  is said to be convergent or converge if there exists an
is said to be convergent or converge if there exists an  such that
such that  for all
for all  . In this case,
. In this case,  is called thelimit of the sequence
is called thelimit of the sequence  and we denote it by
and we denote it by  -
- .
.
Definition 1.3 (see [5, 9, 10]).
Let  be a fuzzy normed vector space. A sequence
be a fuzzy normed vector space. A sequence  in
in  is called Cauchy if for each
is called Cauchy if for each  and each
and each  there exists an
there exists an  such that for all
such that for all  and all
and all  , we have
, we have  .
.
It is wellknown that every convergent sequence in a fuzzy normed vector space is Cauchy. If each Cauchy sequence is convergent, then the fuzzy norm is said to be complete and the fuzzy normed vector space is called a fuzzy Banach space.
We say that a mapping  between fuzzy normed vector spaces
between fuzzy normed vector spaces  and
and  is continuous at a point
is continuous at a point  if for each sequence
if for each sequence  converging to
converging to  in
in  , the sequence
, the sequence  converges to
converges to  . If
. If  is continuous at each
is continuous at each  , then
, then  is said to be continuous on
is said to be continuous on  (see [8]).
(see [8]).
The stability problem of functional equations originated from a question of Ulam [13] concerning the stability of group homomorphisms. Hyers [14] gave a first affirmative partial answer to the question of Ulam for Banach spaces. Hyers' theorem was generalized by Aoki [15] for additive mappings and by Th. M. Rassias [16] for linear mappings by considering an unbounded Cauchy difference. The paper of Th. M. Rassias [16] has provided a lot of influence in the development of what we call generalized Hyers-Ulam stability or as Hyers-Ulam-Rassias stability of functional equations. A generalization of the Th. M. Rassias theorem was obtained by G vruta [17] by replacing the unbounded Cauchy difference by a general control function in the spirit of Th.M. Rassias' approach.
vruta [17] by replacing the unbounded Cauchy difference by a general control function in the spirit of Th.M. Rassias' approach.
The functional equation

is called a quadratic functional equation. In particular, every solution of the quadratic functional equation is said to be aquadratic mapping. A generalized Hyers-Ulam stability problem for the quadratic functional equation was proved by Skof [18] for mappings  , where
, where  is a normed space and
is a normed space and  is a Banach space. Cholewa [19] noticed that the theorem of Skof is still true if the relevant domain
is a Banach space. Cholewa [19] noticed that the theorem of Skof is still true if the relevant domain  is replaced by an Abelian group. Czerwik [20] proved the generalized Hyers-Ulam stability of the quadratic functional equation. The stability problems of several functional equations have been extensively investigated by a number of authors and there are many interesting results concerning this problem (see [16, 21–39]).
is replaced by an Abelian group. Czerwik [20] proved the generalized Hyers-Ulam stability of the quadratic functional equation. The stability problems of several functional equations have been extensively investigated by a number of authors and there are many interesting results concerning this problem (see [16, 21–39]).
In [40], Lee et al. considered the following quartic functional equation:

It is easy to show that the function  satisfies the functional equation (1.3), which is called a quartic functional equation and every solution of the quartic functional equation is said to be a quartic mapping.
satisfies the functional equation (1.3), which is called a quartic functional equation and every solution of the quartic functional equation is said to be a quartic mapping.
Let  be a set. A function
be a set. A function  is called a generalized metric on
is called a generalized metric on  if
if  satisfies
satisfies
(1) if and only if
if and only if  ;
;
(2) for all
for all  ;
;
(3) for all
for all  .
.
We recall a fundamental result in fixed point theory.
Let  be a complete generalized metric space and let
be a complete generalized metric space and let  be a strictly contractive mapping with Lipschitz constant
be a strictly contractive mapping with Lipschitz constant  . Then for each given element
. Then for each given element  , either
, either

for all nonnegative integers  or there exists a positive integer
or there exists a positive integer  such that
such that
(1) ;
;
(2)the sequence  converges to a fixed point
converges to a fixed point  of
of  ;
;
(3) is the unique fixed point of
is the unique fixed point of  in the set
in the set  ;
;
(4) for all
for all  .
.
In 1996, G. Isac and Th. M. Rassias [43] were the first to provide applications of stability theory of functional equations for the proof of new fixed point theorems with applications. By using fixed point methods, the stability problems of several functional equations have been extensively investigated by a number of authors (see [12, 44–48]).
This paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we prove the generalized Hyers-Ulam stability of the additive-quadratic-quartic functional equation (1.1) in fuzzy Banach spaces for an odd case. In Section 3, we prove the generalized Hyers-Ulam stability of the additive-quadratic-quartic functional equation (1.1) in fuzzy Banach spaces for an even case.
Throughout this paper, assume that  is a vector space and that
is a vector space and that  is a fuzzy Banach space.
is a fuzzy Banach space.
2. Generalized Hyers-Ulam Stability of the Functional Equation (1.1): An Odd Case
One can easily show that an odd mapping  satisfies (1.1) if and only if the odd mapping mapping
satisfies (1.1) if and only if the odd mapping mapping  is an additive mapping, that is,
is an additive mapping, that is,

One can easily show that an even mapping  satisfies (1.1) if and only if the even mapping
satisfies (1.1) if and only if the even mapping  is a quadratic-quartic mapping, that is,
is a quadratic-quartic mapping, that is,

It was shown in [49, Lemma 2.1] that  and
and  are quartic and quadratic, respectively, and that
are quartic and quadratic, respectively, and that  .
.
For a given mapping  , we define
, we define

for all  .
.
Using the fixed point method, we prove the generalized Hyers-Ulam stability of the functional equation  in fuzzy Banach spaces: an odd case.
in fuzzy Banach spaces: an odd case.
Theorem 2.1.
Let  be a function such that there exists an
be a function such that there exists an  with
with

for all  . Let
. Let  be an odd mapping satisfying
be an odd mapping satisfying

for all  and all
and all  . Then
. Then

exists for each  and defines an additive mapping
and defines an additive mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
Letting  in (2.5), we get
in (2.5), we get

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Consider the set

and introduce the generalized metric on 

where, as usual,  . It is easy to show that
. It is easy to show that  is complete. (see the proof of Lemma 2.1 of [50].)
is complete. (see the proof of Lemma 2.1 of [50].)
Now we consider the linear mapping  such that
such that

for all  .
.
Let  be given such that
be given such that  . Then
. Then

for all  and all
and all  . Hence
. Hence

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  implies that
implies that  . This means that
. This means that

for all  .
.
It follows from (2.8) that

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  .
.
By Theorem 1.4, there exists a mapping  satisfying the following.
satisfying the following.
-
(1)

is a fixed point of
 , that is,
, that is,

for all  . Since
. Since  is odd,
is odd,  is an odd mapping. The mapping
is an odd mapping. The mapping  is a unique fixed point of
is a unique fixed point of  in the set
in the set

This implies that  is a unique mapping satisfying (2.16) such that there exists a
is a unique mapping satisfying (2.16) such that there exists a  satisfying
satisfying

for all  and all
and all  .
.
-
(2)

as
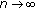 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality

for all  ;
;
-
(3)

, which implies the inequality

This implies that inequality (2.7) holds.
By (2.5),

for all  , all
, all  and all
and all  . So
. So

for all  , all
, all  and all
and all  . Since
. Since  for all
for all  and all
and all  ,
,

for all  and all
and all  . Thus the mapping
. Thus the mapping  is additive, as desired.
is additive, as desired.
Corollary 2.2.
Let  and let
and let  be a real number with
be a real number with  . Let
. Let  be a normed vector space with norm
be a normed vector space with norm  . Let
. Let  be an odd mapping satisfying
be an odd mapping satisfying

for all  and all
and all  . Then
. Then

exists for each  and defines an additive mapping
and defines an additive mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
The proof follows from Theorem 2.1 by taking

for all  . Then we can choose
. Then we can choose  and we get the desired result.
and we get the desired result.
Theorem 2.3.
Let  be a function such that there exists an
be a function such that there exists an  with
with

for all  . Let
. Let  be an odd mapping satisfying (2.5). Then
be an odd mapping satisfying (2.5). Then

exists for each  and defines an additive mapping
and defines an additive mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
Let  be the generalized metric space defined in the proof of Theorem 2.1.
be the generalized metric space defined in the proof of Theorem 2.1.
Consider the linear mapping  such that
such that

for all  .
.
Let  be given such that
be given such that  . Then
. Then

for all  and all
and all  . Hence
. Hence

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  implies that
implies that  . This means that
. This means that

for all  .
.
It follows from (2.8) that

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  .
.
By Theorem 1.4, there exists a mapping  satisfying the following.
satisfying the following.
-
(1)

is a fixed point of
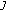 , that is,
, that is,

for all  . Since
. Since  is odd,
is odd,  is an odd mapping. The mapping
is an odd mapping. The mapping  is a unique fixed point of
is a unique fixed point of  in the set
in the set

This implies that  is a unique mapping satisfying (2.36) such that there exists a
is a unique mapping satisfying (2.36) such that there exists a  satisfying
satisfying

for all  and all
and all  .
.
-
(2)
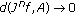
as
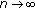 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality

for all  ;
;
-
(3)
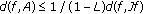
, which implies the inequality

This implies that the inequality (2.30) holds.
The rest of the proof is similar to the proof of Theorem 2.1.
Corollary 2.4.
Let  and let
and let  be a real number with
be a real number with  . Let
. Let  be a normed vector space with norm
be a normed vector space with norm  . Let
. Let  be an odd mapping satisfying (2.24). Then
be an odd mapping satisfying (2.24). Then

exists for each  and defines an additive mapping
and defines an additive mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
The proof follows from Theorem 2.3 by taking

for all  . Then we can choose
. Then we can choose  and we get the desired result.
and we get the desired result.
3. Generalized Hyers-Ulam Stability of the Functional Equation (1.1):An Even Case
Using the fixed point method, we prove the generalized Hyers-Ulam stability of the functional equation  in fuzzy Banach spaces: an even case.
in fuzzy Banach spaces: an even case.
Theorem 3.1.
Let  be a function such that there exists an
be a function such that there exists an  with
with

for all  . Let
. Let  be an even mapping satisfying
be an even mapping satisfying  and (2.5). Then
and (2.5). Then

exists for each  and defines a quartic mapping
and defines a quartic mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
Letting  in (2.5), we get
in (2.5), we get

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Replacing  by
by  in (2.5), we get
in (2.5), we get

for all  and all
and all  .
.
By (3.4) and (3.5),

for all  and all
and all  . Letting
. Letting  for all
for all  , we get
, we get

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Consider the set

and introduce the generalized metric on 

where, as usual,  . It is easy to show that
. It is easy to show that  is complete. (see the proof of Lemma 2.1 of [50]).
is complete. (see the proof of Lemma 2.1 of [50]).
Now we consider the linear mapping  such that
such that

for all  .
.
Let  be given such that
be given such that  . Then
. Then

for all  and all
and all  . Hence
. Hence

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  implies that
implies that  . This means that
. This means that

for all  .
.
It follows from (3.7) that

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  .
.
By Theorem 1.4, there exists a mapping  satisfying the following.
satisfying the following.
-
(1)
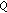
is a fixed point of
 , that is,
, that is,

for all  . Since
. Since  is even,
is even,  is an even mapping. The mapping
is an even mapping. The mapping  is a unique fixed point of
is a unique fixed point of  in the set
in the set

This implies that  is a unique mapping satisfying (3.15) such that there exists a
is a unique mapping satisfying (3.15) such that there exists a  satisfying
satisfying

for all  and all
and all  .
.
-
(2)
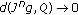
as
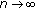 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality

for all  .
.
-
(3)
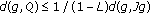
, which implies the inequality

This implies that inequality (3.3) holds.
The rest of the proof is similar to that of the proof of Theorem 2.1.
Corollary 3.2.
Let  and let
and let  be a real number with
be a real number with  . Let
. Let  be a normed vector space with norm
be a normed vector space with norm  . Let
. Let  be an even mapping satisfying
be an even mapping satisfying  and (2.24). Then
and (2.24). Then

exists for each  and defines a quartic mapping
and defines a quartic mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
The proof follows from Theorem 3.1 by taking

for all  . Then we can choose
. Then we can choose  and we get the desired result.
and we get the desired result.
Theorem 3.3.
Let  be a function such that there exists an
be a function such that there exists an  with
with

for all  . Let
. Let  be an even mapping satisfying
be an even mapping satisfying  and (2.5). Then
and (2.5). Then

exists for each  and defines a quartic mapping
and defines a quartic mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
Let  be the generalized metric space defined in the proof of Theorem 3.1.
be the generalized metric space defined in the proof of Theorem 3.1.
Consider the linear mapping  such that
such that

for all  .
.
Let  be given such that
be given such that  . Then
. Then

for all  and all
and all  . Hence
. Hence

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  implies that
implies that  . This means that
. This means that

for all  .
.
It follows from (3.7) that

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  .
.
By Theorem 1.4, there exists a mapping  satisfying the following.
satisfying the following.
-
(1)
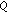
is a fixed point of
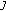 , that is,
, that is,

for all  . Since
. Since  is even,
is even,  is an even mapping. The mapping
is an even mapping. The mapping  is a unique fixed point of
is a unique fixed point of  in the set
in the set

This implies that  is a unique mapping satisfying (3.31) such that there exists a
is a unique mapping satisfying (3.31) such that there exists a  satisfying
satisfying

for all  and all
and all  .
.
-
(2)

as
 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality

for all  ;
;
-
(3)
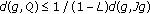
, which implies the inequality

This implies that inequality (3.25) holds.
The rest of the proof is similar to that of the proof of Theorem 2.1.
Corollary 3.4.
Let  and let
and let  be a real number with
be a real number with  . Let
. Let  be a normed vector space with norm
be a normed vector space with norm  . Let
. Let  be an even mapping satisfying
be an even mapping satisfying  and (2.24). Then
and (2.24). Then

exists for each  and defines a quartic mapping
and defines a quartic mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
The proof follows from Theorem 3.3 by taking

for all  . Then we can choose
. Then we can choose  and we get the desired result.
and we get the desired result.
Theorem 3.5.
Let  be a function such that there exists an
be a function such that there exists an  with
with

for all  . Let
. Let  be an even mapping satisfying
be an even mapping satisfying  and (2.5). Then
and (2.5). Then

exists for each  and defines a quadratic mapping
and defines a quadratic mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
Let  be the generalized metric space defined in the proof of Theorem 3.1.
be the generalized metric space defined in the proof of Theorem 3.1.
Letting  for all
for all  in (3.6), we get
in (3.6), we get

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Now we consider the linear mapping  such that
such that

for all  .
.
Let  be given such that
be given such that  . Then
. Then

for all  and all
and all  . Hence
. Hence

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  implies that
implies that  . This means that
. This means that

for all  .
.
It follows from (3.42) that

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  .
.
By Theorem 1.4, there exists a mapping  satisfying the following.
satisfying the following.
-
(1)
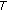
is a fixed point of
 , that is,
, that is,

for all  . Since
. Since  is even,
is even,  is an even mapping. The mapping
is an even mapping. The mapping  is a unique fixed point of
is a unique fixed point of  in the set
in the set

This implies that  is a unique mapping satisfying (3.48) such that there exists a
is a unique mapping satisfying (3.48) such that there exists a  satisfying
satisfying

for all  and all
and all  .
.
-
(2)

as
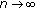 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality

for all  .
.
-
(3)
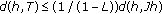
, which implies the inequality

This implies that inequality (3.41) holds.
The rest of the proof is similar to that of the proof of Theorem 2.1.
Corollary 3.6.
Let  and let
and let  be a real number with
be a real number with  . Let
. Let  be a normed vector space with norm
be a normed vector space with norm  . Let
. Let  be an even mapping satisfying
be an even mapping satisfying  and (2.24). Then
and (2.24). Then

exists for each  and defines a quadratic mapping
and defines a quadratic mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
The proof follows from Theorem 3.5 by taking

for all  . Then we can choose
. Then we can choose  and we get the desired result.
and we get the desired result.
Theorem 3.7.
Let  be a function such that there exists an
be a function such that there exists an  with
with

for all  . Let
. Let  be an even mapping satisfying
be an even mapping satisfying  and (2.5). Then
and (2.5). Then

exists for each  and defines a quadratic mapping
and defines a quadratic mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
Let  be the generalized metric space defined in the proof of Theorem 3.1.
be the generalized metric space defined in the proof of Theorem 3.1.
Consider the linear mapping  such that
such that

for all  .
.
Let  be given such that
be given such that  . Then
. Then

for all  and all
and all  . Hence
. Hence

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  implies that
implies that  . This means that
. This means that

for all  .
.
It follows from (3.42) that

for all  and all
and all  . So
. So  .
.
By Theorem 1.4, there exists a mapping  satisfying the following.
satisfying the following.
-
(1)
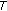
is a fixed point of
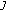 , that is,
, that is,

for all  . Since
. Since  is even,
is even,  is an even mapping. The mapping
is an even mapping. The mapping  is a unique fixed point of
is a unique fixed point of  in the set
in the set

This implies that  is a unique mapping satisfying (3.64) such that there exists a
is a unique mapping satisfying (3.64) such that there exists a  satisfying
satisfying

for all  and all
and all  .
.
-
(2)
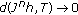
as
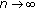 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality

for all  .
.
-
(3)
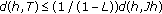
, which implies the inequality

This implies that inequality (3.58) holds.
The rest of the proof is similar to that of the proof of Theorem 2.1.
Corollary 3.8.
Let  and let
and let  be a real number with
be a real number with  . Let
. Let  be a normed vector space with norm
be a normed vector space with norm  . Let
. Let  be an even mapping satisfying
be an even mapping satisfying  and (2.24). Then
and (2.24). Then

exists for each  and defines a quadratic mapping
and defines a quadratic mapping  such that
such that

for all  and all
and all  .
.
Proof.
The proof follows from Theorem 3.7 by taking

for all  . Then we can choose
. Then we can choose  and we get the desired result.
and we get the desired result.
References
Katsaras AK: Fuzzy topological vector spaces. II. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 1984, 12(2):143–154. 10.1016/0165-0114(84)90034-4
Felbin C: Finite-dimensional fuzzy normed linear space. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 1992, 48(2):239–248. 10.1016/0165-0114(92)90338-5
Krishna SV, Sarma KKM: Separation of fuzzy normed linear spaces. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 1994, 63(2):207–217. 10.1016/0165-0114(94)90351-4
Xiao J-Z, Zhu X-H: Fuzzy normed space of operators and its completeness. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2003, 133(3):389–399. 10.1016/S0165-0114(02)00274-9
Bag T, Samanta SK: Finite dimensional fuzzy normed linear spaces. Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics 2003, 11(3):687–705.
Cheng SC, Mordeson JN: Fuzzy linear operators and fuzzy normed linear spaces. Bulletin of the Calcutta Mathematical Society 1994, 86(5):429–436.
Kramosil I, Michálek J: Fuzzy metrics and statistical metric spaces. Kybernetika 1975, 11(5):336–344.
Bag T, Samanta SK: Fuzzy bounded linear operators. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2005, 151(3):513–547. 10.1016/j.fss.2004.05.004
Mirmostafaee AK, Mirzavaziri M, Moslehian MS: Fuzzy stability of the Jensen functional equation. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2008, 159(6):730–738. 10.1016/j.fss.2007.07.011
Mirmostafaee AK, Moslehian MS: Fuzzy versions of Hyers-Ulam-Rassias theorem. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 2008, 159(6):720–729. 10.1016/j.fss.2007.09.016
Mirmostafaee AK, Moslehian MS: Fuzzy approximately cubic mappings. Information Sciences 2008, 178(19):3791–3798. 10.1016/j.ins.2008.05.032
Mirzavaziri M, Moslehian MS: A fixed point approach to stability of a quadratic equation. Bulletin of the Brazilian Mathematical Society 2006, 37(3):361–376. 10.1007/s00574-006-0016-z
Ulam SM: A Collection of Mathematical Problems, Interscience Tracts in Pure and Applied Mathematics, no. 8. Interscience, New York, NY, USA; 1960:xiii+150.
Hyers DH: On the stability of the linear functional equation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1941, 27: 222–224. 10.1073/pnas.27.4.222
Aoki T: On the stability of the linear transformation in Banach spaces. Journal of the Mathematical Society of Japan 1950, 2: 64–66. 10.2969/jmsj/00210064
Rassias ThM: On the stability of the linear mapping in Banach spaces. Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society 1978, 72(2):297–300. 10.1090/S0002-9939-1978-0507327-1
Găvruţa P: A generalization of the Hyers-Ulam-Rassias stability of approximately additive mappings. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 1994, 184(3):431–436. 10.1006/jmaa.1994.1211
Skof F: Local properties and approximation of operators. Rendiconti del Seminario Matematico e Fisico di Milano 1983, 53: 113–129. 10.1007/BF02924890
Cholewa PW: Remarks on the stability of functional equations. Aequationes Mathematicae 1984, 27(1–2):76–86.
Czerwik St: On the stability of the quadratic mapping in normed spaces. Abhandlungen aus dem Mathematischen Seminar der Universität Hamburg 1992, 62: 59–64. 10.1007/BF02941618
Baktash E, Cho YJ, Jalili M, Saadati R, Vaezpour SM: On the stability of cubic mappings and quadratic mappings in random normed spaces. Journal of Inequalities and Applications 2008, 2008:-11.
Eshaghi-Gordji M, Kaboli-Gharetapeh S, Park C, Zolfaghri S: Stability of an additive-cubic-quartic functional equation. Advances in Difference Equations to appear to appear
Hyers DH, Isac G, Rassias TM: Stability of Functional Equations in Several Variables, Progress in Nonlinear Differential Equations and Their Applications. Volume 34. Birkhäuser, Boston, Mass, USA; 1998:vi+313.
Jun K-W, Kim H-M: The generalized Hyers-Ulam-Rassias stability of a cubic functional equation. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2002, 274(2):267–278.
Jung S-M: Hyers-Ulam-Rassias Stability of Functional Equations in Mathematical Analysis. Hadronic, Palm Harbor, Fla, USA; 2001:ix+256.
Park C: Hyers-Ulam-Rassias stability of homomorphisms in quasi-Banach algebras. Bulletin des Sciences Mathématiques 2008, 132(2):87–96.
Park C, Cui J: Generalized stability of -ternary quadratic mappings. Abstract and Applied Analysis 2007, 2007:-6.
Park C, Najati A: Homomorphisms and derivations in -algebras. Abstract and Applied Analysis 2007, 2007:-12.
Rassias JM: On approximation of approximately linear mappings by linear mappings. Bulletin des Sciences Mathématiques 1984, 108(4):445–446.
Rassias JM: Refined Hyers-Ulam approximation of approximately Jensen type mappings. Bulletin des Sciences Mathématiques 2007, 131(1):89–98.
Rassias JM, Rassias MJ: Asymptotic behavior of alternative Jensen and Jensen type functional equations. Bulletin des Sciences Mathématiques 2005, 129(7):545–558.
Rassias ThM: Problem 16; 2, report of the 27th International Symposium on Functional Equations. Aequationes Mathematicae 1990, 39(2–3):292–293.
Rassias ThM: On the stability of the quadratic functional equation and its applications. Studia Universitatis Babes-Bolyai 1998, 43(3):89–124.
Rassias ThM: The problem of S. M. Ulam for approximately multiplicative mappings. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2000, 246(2):352–378. 10.1006/jmaa.2000.6788
Rassias ThM: On the stability of functional equations in Banach spaces. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2000, 251(1):264–284. 10.1006/jmaa.2000.7046
Rassias ThM: On the stability of functional equations and a problem of Ulam. Acta Applicandae Mathematicae 2000, 62(1):23–130. 10.1023/A:1006499223572
Rassias ThM, Šemrl P: On the behavior of mappings which do not satisfy Hyers-Ulam stability. Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society 1992, 114(4):989–993. 10.1090/S0002-9939-1992-1059634-1
Rassias ThM, Šemrl P: On the Hyers-Ulam stability of linear mappings. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 1993, 173(2):325–338. 10.1006/jmaa.1993.1070
Rassias ThM, Shibata K: Variational problem of some quadratic functionals in complex analysis. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 1998, 228(1):234–253. 10.1006/jmaa.1998.6129
Lee SH, Im SM, Hwang IS: Quartic functional equations. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2005, 307(2):387–394. 10.1016/j.jmaa.2004.12.062
Cădariu L, Radu V: Fixed points and the stability of Jensen's functional equation. Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics 2003., 4(1):
Diaz JB, Margolis B: A fixed point theorem of the alternative, for contractions on a generalized complete metric space. Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society 1968, 74: 305–309. 10.1090/S0002-9904-1968-11933-0
Isac G, Rassias ThM: Stability of -additive mappings: applications to nonlinear analysis. International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences 1996, 19(2):219–228. 10.1155/S0161171296000324
Cădariu L, Radu V: On the stability of the Cauchy functional equation: a fixed point approach. In Iteration Theory, Grazer Mathematische Berichte. Volume 346. Karl-Franzens-Universitaet, Graz, Austria; 2004:43–52.
Cădariu L, Radu V: Fixed point methods for the generalized stability of functional equations in a single variable. Fixed Point Theory and Applications 2008, 2008:-15.
Park C: Fixed points and Hyers-Ulam-Rassias stability of Cauchy-Jensen functional equations in Banach algebras. Fixed Point Theory and Applications 2007, 2007:-15.
Park C: Generalized Hyers-Ulam stability of quadratic functional equations: a fixed point approach. Fixed Point Theory and Applications 2008, 2008:-9.
Radu V: The fixed point alternative and the stability of functional equations. Fixed Point Theory 2003, 4(1):91–96.
Eshaghi-Gordji M, Abbaszadeh S, Park C: On the stability of a generalized quadratic and quartic type functional equation in quasi-Banach spaces. Journal of Inequalities and Applications 2009, 2009:-26.
Miheţ D, Radu V: On the stability of the additive Cauchy functional equation in random normed spaces. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2008, 343(1):567–572.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Hanyang University in 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, C. Fuzzy Stability of an Additive-Quadratic-Quartic Functional Equation. J Inequal Appl 2010, 253040 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/253040
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/253040

 , that is,
, that is,
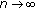 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality

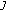 , that is,
, that is,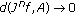
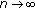 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality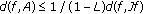
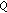
 , that is,
, that is,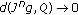
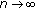 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality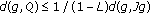
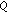
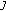 , that is,
, that is,
 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality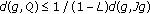
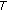
 , that is,
, that is,
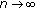 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality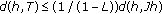
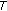
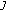 , that is,
, that is,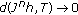
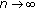 . This implies the equality
. This implies the equality