- Research Article
- Open access
- Published:
On Refinements of Aczél, Popoviciu, Bellman's Inequalities and Related Results
Journal of Inequalities and Applications volume 2010, Article number: 579567 (2010)
Abstract
We give some refinements of the inequalities of Aczél, Popoviciu, and Bellman. Also, we give some results related to power sums.
1. Introduction
The well-known Aczél's inequality [1] (see also [2, page 117]) is given in the following result.
Theorem 1.1.
Let  be a fixed positive integer, and let
be a fixed positive integer, and let  be real numbers such that
be real numbers such that

then

with equality if and only if the sequences  and
and  are proportional.
are proportional.
A related result due to Bjelica [3] is stated in the following theorem.
Theorem 1.2.
Let  be a fixed positive integer, and let
be a fixed positive integer, and let  be nonnegative real numbers such that
be nonnegative real numbers such that

then, for  , one has
, one has

Note that quotation of the above result in [4, page 58] is mistakenly stated for all  . In 1990, Bjelica [3] proved that the above result is true for
. In 1990, Bjelica [3] proved that the above result is true for  . Mascioni [5], in 2002, gave the proof for
. Mascioni [5], in 2002, gave the proof for  and gave the counter example to show that the above result is not true for
and gave the counter example to show that the above result is not true for  . Díaz-Barreo et al. [6] mistakenly stated it for positive integer
. Díaz-Barreo et al. [6] mistakenly stated it for positive integer  and gave a refinement of the inequality (1.4) as follows.
and gave a refinement of the inequality (1.4) as follows.
Theorem 1.3.
Let  be positive integers, and let
be positive integers, and let  be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied, then for
be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied, then for  , one has
, one has

where

Moreover, Díaz-Barreo et al. [6] stated the above result as Popoviciu's generalization of Aczél's inequality given in [7]. In fact, generalization of inequality (1.2) attributed to Popoviciu [7] is stated in the following theorem (see also [2, page 118]).
Theorem 1.4.
Let  be a fixed positive integer, and let
be a fixed positive integer, and let  be nonnegative real numbers such that
be nonnegative real numbers such that

Also, let  , then, for
, then, for  , one has
, one has

If  , then reverse of the inequality (1.8) holds.
, then reverse of the inequality (1.8) holds.
The well-known Bellman's inequality is stated in the following theorem [8] (see also [2, pages 118-119]).
Theorem 1.5.
Let  be a fixed positive integer, and let
be a fixed positive integer, and let  be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied. If
be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied. If  , then
, then

Díaz-Barreo et al. [6] gave a refinement of the above inequality for positive integer  . They proved the following result.
. They proved the following result.
Theorem 1.6.
Let  be positive integers, and let
be positive integers, and let  ,
,  be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied, then for
be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied, then for  , one has
, one has

where

In this paper, first we give a simple extension of a Theorem 1.2 with Aczél's inequality. Further, we give refinements of Theorems 1.2, 1.4, and 1.5. Also, we give some results related to power sums.
2. Main Results
To give extension of Theorem 1.2, we will use the result proved by Pečarić and Vasić in 1979 [9, page 165].
Lemma 2.1.
Let  be nonnegative real numbers such that
be nonnegative real numbers such that  , then for
, then for  , one has
, one has

Theorem 2.2.
Let  be a fixed positive integer, and let
be a fixed positive integer, and let  be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied, then, for
be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied, then, for  , one has
, one has

Proof.
By using condition (1.3) in Lemma 2.1 for  , we have
, we have

These imply

Now, applying Azcél's inequality on right-hand side of the above inequality gives us the required result.
Let  and
and  be positive real numbers such that
be positive real numbers such that  , then the well-known Hölder's inequality states that
, then the well-known Hölder's inequality states that

where  are positive real numbers.
are positive real numbers.
If  , then the well-known inequality of power sums of order
, then the well-known inequality of power sums of order  and
and  states that
states that

where  are positive real numbers (c.f [9, page 165]).
are positive real numbers (c.f [9, page 165]).
Now, if  , then
, then  and using inequality (2.6) in (2.5), we get
and using inequality (2.6) in (2.5), we get

We use the inequality (2.7) and the Hölder's inequality to prove the further refinements of the Theorems 1.2 and 1.4.
Theorem 2.3.
Let  and
and  be fixed positive integers such that
be fixed positive integers such that  , and let
, and let  be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied. Let one denote
be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied. Let one denote

(i)If  , then
, then

(ii)If  , then
, then

Proof.
-
(i)
First of all, we observe that
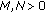 and also
and also 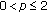 , therefore by Theorem 1.2, we have
, therefore by Theorem 1.2, we have

We can write

By applying Theorem 1.2 for  on right-hand side of the above equation, we get
on right-hand side of the above equation, we get

By using inequality (2.11) on right-hand side of the above expression follows the required result.
-
(ii)
Since

and denoting  ,
,  ,
,
then

It is given that  and
and  , therefore by using Theorem 1.2, for
, therefore by using Theorem 1.2, for  , on right-hand side of the above equation, we get
, on right-hand side of the above equation, we get

since  , so by using (2.7)
, so by using (2.7)

Theorem 2.4.
Let  and
and  be fixed positive integers such that
be fixed positive integers such that  , and let
, and let  be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.7) is satisfied. Also let
be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.7) is satisfied. Also let  ,
,  be defined in (2.8) and
be defined in (2.8) and

then, for  , one has
, one has

Proof.
First of all, note that  , therefore by generalized Aczél's inequality, we have
, therefore by generalized Aczél's inequality, we have

Now,

and denote  ,
,  .
.
Then

It is given that  and
and  , therefore by using Theorem 1.4, for
, therefore by using Theorem 1.4, for  , on right-hand side of the above equation, we get
, on right-hand side of the above equation, we get

by applying Hölder's inequality

by using inequality (2.20)

In [6], a refinement of Bellman's inequality is given for positive integer  ; here, we give further refinements of Bellman's inequality for real
; here, we give further refinements of Bellman's inequality for real  . We will use Minkowski's inequality in the proof and recall that, for real
. We will use Minkowski's inequality in the proof and recall that, for real  and for positive reals
and for positive reals  , the Minkowski's inequality states that
, the Minkowski's inequality states that

Theorem 2.5.
Let  and
and  be fixed positive integers such that
be fixed positive integers such that  , and let
, and let  be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied. Also let
be nonnegative real numbers such that (1.3) is satisfied. Also let  and
and  be defined in (2.8). If
be defined in (2.8). If  , then
, then

Proof.
First of all, note that  and
and  , therefore by using Bellman's inequality, we have
, therefore by using Bellman's inequality, we have

Now,

and denote  ,
,  .
.
Then

It is given that  and
and  , therefore by using Bellman's inequality, for
, therefore by using Bellman's inequality, for  , on right-hand side of the above equation, we get
, on right-hand side of the above equation, we get

by applying Minkowski's inequality

and by using inequality (2.28)

Remark 2.6.
In [10], Hu and Xu gave the generalized results related to Theorems 2.4 and 2.5.
3. Some Further Remarks on Power Sums
The following theorem [9, page 152] is very useful to give results related to power sums in connection with results given in [11, 12].
Theorem 3.1.
Let  , where
, where  is interval in
is interval in  and
and  . Also let
. Also let  be a function such that
be a function such that  is increasing on
is increasing on  , then
, then

Remark 3.2.
If  is strictly increasing on
is strictly increasing on  , then strict inequality holds in (3.1).
, then strict inequality holds in (3.1).
Here, it is important to note that if we consider

then  is increasing on
is increasing on  for
for  . By using it in Theorem 3.1, we get
. By using it in Theorem 3.1, we get

This implies Lemma 2.1 by substitution,  .
.
In this section, we use Theorem 3.1 to give some results related to power sums as given in [11–13], but here we will discuss only the nonweighted case.
In [11], we introduced Cauchy means related to power sums; here, we restate the means without weights.
Let  be a positive
be a positive  -tuple, then for
-tuple, then for  we defined
we defined

We proved that  is monotonically increasing with respect to
is monotonically increasing with respect to  and
and  .
.
In this section, we give exponential convexity of a positive difference of the inequality (3.1) by using parameterized class of functions. We define new means and discuss their relation to the means defined in [11]. Also, we prove mean value theorem of Cauchy type.
It is worthwhile to recall the following.
Definition 3.3.
A function  is exponentially convex if it is continuous and
is exponentially convex if it is continuous and

for all  and all choices
and all choices  , and
, and  , such that
, such that  .
.
Proposition 3.4.
Let  . The following propositions are equivalent:
. The following propositions are equivalent:
(i) is exponentially convex,
is exponentially convex,
(ii) is continuous and
is continuous and

for every  and for every
and for every  ,
,  .
.
Corollary 3.5.
If  is exponentially convex function, then
is exponentially convex function, then  is a log-convex function.
is a log-convex function.
3.1. Exponential Convexity
Lemma 3.6.
Let  and
and  be the function defined as
be the function defined as

then  is strictly increasing function on
is strictly increasing function on  for each
for each  .
.
Proof.
Since

therefore  is strictly increasing function on
is strictly increasing function on  for each
for each  .
.
Theorem 3.7.
Let  be a positive
be a positive  -tuple
-tuple  such that
such that  , and let
, and let

(a)For  , let
, let  be arbitrary real numbers, then the matrix
be arbitrary real numbers, then the matrix

is a positive semidefinite matrix.
(b)The function  is exponentially convex.
is exponentially convex.
(c)The function  is log convex.
is log convex.
Proof.
-
(a)
Define a function
 (3.11)
(3.11)
then

This implies that  is increasing function on
is increasing function on  . So using
. So using  in the place of
in the place of  in (3.1), we have
in (3.1), we have

Hence, the given matrix is positive semidefinite.
-
(b)
Since after some computation we have that
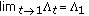 so
so is continuous on
is continuous on  , then by Proposition 3.4, we have that
, then by Proposition 3.4, we have that 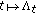 is exponentially convex.
is exponentially convex. -
(c)
Since
 is strictly increasing function on
is strictly increasing function on 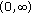 , so by Remark 3.2, we have
, so by Remark 3.2, we have  (3.14)
(3.14)
it follows that  . Now, by Corollary 3.5, we have that
. Now, by Corollary 3.5, we have that  is log convex.
is log convex.
Let us introduce the following.
Definition 3.8.
Let  be a positive
be a positive  -tuple
-tuple  such that
such that  for
for  , then for
, then for  , we define
, we define

Remark 3.9.
Let us note that  ,
,  , and
, and  .
.
Remark 3.10.
If in  we substitute
we substitute  by
by  , then we get
, then we get  , and if we substitute
, and if we substitute  by
by  in
in  , we get
, we get  .
.
In [11], we have the following lemma.
Lemma 3.11.
Let  be a log-convex function and assume that if
be a log-convex function and assume that if  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , then the following inequality is valid:
, then the following inequality is valid:

Theorem 3.12 ..
Let  be positive
be positive  -tuple
-tuple  such that
such that  for
for  , then for
, then for  such that
such that  ,
,  , one has
, one has

Proof.
Let  be defined by (3.9). Now taking
be defined by (3.9). Now taking  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , where
, where  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  in Lemma 3.11, we have
in Lemma 3.11, we have

Since  , by substituting
, by substituting  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  , where
, where  , in above inequality, we get
, in above inequality, we get

By raising power  , we get (3.17) for
, we get (3.17) for  ,
,  and
and  .
.
From Remark 3.9, we get that (3.17) is also valid for  or
or  or
or  .
.
Remark 3.13.
If we substitute  by
by  , then monotonicity of
, then monotonicity of  implies the monotonicity of
implies the monotonicity of  , and if we substitute
, and if we substitute  by
by  , then monotonicity of
, then monotonicity of  implies monotonicity of
implies monotonicity of  .
.
3.2. Mean Value Theorems
We will use the following lemma [11] to prove the related mean value theorems of Cauchy type.
Lemma 3.14.
Let  , where
, where  such that
such that

Consider the functions  ,
,  defined as
defined as

then  for
for  are monotonically increasing functions.
are monotonically increasing functions.
Theorem 3.15.
Let  , where
, where  is a compact interval such that
is a compact interval such that  and
and  . If
. If  , then there exists
, then there exists  such that
such that

Proof.
Since  is compact and
is compact and  , therefore let
, therefore let

In Theorem 3.1, setting  and
and  , respectively, as defined in Lemma 3.14, we get the following inequalities:
, respectively, as defined in Lemma 3.14, we get the following inequalities:

If  , then
, then  is strictly increasing function on
is strictly increasing function on  , therefore by Theorem 3.1, we have
, therefore by Theorem 3.1, we have

Now, by combining inequalities (3.24), we get

Finally, by condition (3.20), there exists  , such that
, such that

as required.
Theorem 3.16.
Let  , where
, where  is a compact interval such that
is a compact interval such that  and
and  . If
. If  , then there exists
, then there exists  such that the following equality is true:
such that the following equality is true:

provided that the denominators are nonzero.
Proof.
Let a function  be defined as
be defined as

where  and
and  are defined as
are defined as

Then, using Theorem 3.15, with  , we have
, we have

Since  , therefore (3.31) gives
, therefore (3.31) gives

Putting in (3.30), we get (3.28).
References
Aczél J: Some general methods in the theory of functional equations in one variable. New applications of functional equations. Uspekhi Matematicheskikh Nauk 1956, 11(3(69)):3–68.
Mitrinović DS, Pečarić JE, Fink AM: Classical and New Inequalities in Analysis. Volume 61. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, The Netherlands; 1993:xviii+740.
Bjelica M: On inequalities for indefinite form. L'Analyse Numérique et la Théorie de l'Approximation 1990, 19(2):105–109.
Mitrinović DS: Analytic Inequalities. Springer, New York, NY, USA; 1970:xii+400.
Mascioni V: A note on Aczél type inequalities. Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics 2002., 3(5, article 69):
Díaz-Barrero JL, Grau-Sánchez M, Popescu PG: Refinements of Aczél, Popoviciu and Bellman's inequalities. Computers & Mathematics with Applications 2008, 56(9):2356–2359. 10.1016/j.camwa.2008.05.013
Popoviciu JT: On an inequality. Gazeta Matematica si Fizica A 1959, 11(64):451–461.
Bellman R: On an inequality concerning an indefinite form. The American Mathematical Monthly 1956, 63: 108–109. 10.2307/2306434
Pečarić JE, Proschan F, Tong YL: Convex functions, partial orderings, and statistical applications, Mathematics in Science and Engineering. Volume 187. Academic Press, Boston, Mass, USA; 1992:xiv+467.
Hu Z, Xu A: Refinements of Aczél and Bellman's inequalities. Computers & Mathematics with Applications 2010, 59(9):3078–3083. 10.1016/j.camwa.2010.02.027
Pečarić J, Rehman AtiqUr: On logarithmic convexity for power sums and related results. Journal of Inequalities and Applications 2008, -9.
Pečarić J, ur Rehman A: On logarithmic convexity for power sums and related results. II. Journal of Inequalities and Applications 2008, 2008:-12.
Anwar M, Jakšetić , Pečarić J, ur Rehman A: Exponential convexity, positive semi-definite matrices and fundamental inequalities. Journal of Mathematical Inequalities 2010, 4(2):171–189.
Acknowledgments
This research was partially funded by Higher Education Commission, Pakistan. The research of the second author was supported by the Croatian Ministry of Science, Education and Sports under the Research Grant no. 117-1170889-0888.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Farid, G., Pečarić, J. & Rehman, A. On Refinements of Aczél, Popoviciu, Bellman's Inequalities and Related Results. J Inequal Appl 2010, 579567 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/579567
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/579567
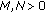 and also
and also 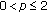 , therefore by Theorem 1.2, we have
, therefore by Theorem 1.2, we have
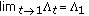 so
so is continuous on
is continuous on  , then by Proposition 3.4, we have that
, then by Proposition 3.4, we have that 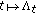 is exponentially convex.
is exponentially convex. is strictly increasing function on
is strictly increasing function on 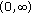 , so by Remark 3.2, we have
, so by Remark 3.2, we have 