- Research Article
- Open access
- Published:
General Nonlinear Random Equations with Random Multivalued Operator in Banach Spaces
Journal of Inequalities and Applications volume 2009, Article number: 865093 (2009)
Abstract
We introduce and study a new class of general nonlinear random multivalued operator equations involving generalized  -accretive mappings in Banach spaces. By using the Chang's lemma and the resolvent operator technique for generalized
-accretive mappings in Banach spaces. By using the Chang's lemma and the resolvent operator technique for generalized  -accretive mapping due to Huang and Fang (2001), we also prove the existence theorems of the solution and convergence theorems of the generalized random iterative procedures with errors for this nonlinear random multivalued operator equations in
-accretive mapping due to Huang and Fang (2001), we also prove the existence theorems of the solution and convergence theorems of the generalized random iterative procedures with errors for this nonlinear random multivalued operator equations in  -uniformly smooth Banach spaces. The results presented in this paper improve and generalize some known corresponding results in iterature.
-uniformly smooth Banach spaces. The results presented in this paper improve and generalize some known corresponding results in iterature.
1. Introduction and Preliminaries
The variational principle has been one of the major branches of mathematical sciences for more than two centuries. It is a tool of great power that can be applied to a wide variety of problems in pure and applied sciences. It can be used to interpret the basic principles of mathematical and physical sciences in the form of simplicity and elegance. During this period, the variational principles have played an important and significant part as a unifying influence in pure and applied sciences and as a guide in the mathematical interpretation of many physical phenomena. The variational principles have played a fundamental role in the development of the general theory of relativity, gauge field theory in modern particle physics and soliton theory. In recent years, these principles have been enriched by the discovery of the variational inequality theory, which is mainly due to Hartman and Stampacchia [1]. Variational inequality theory constituted a significant extension of the variational principles and describes a broad spectrum of very interesting developments involving a link among various fields of mathematics, physics, economics, regional, and engineering sciences. The ideas and techniques are being applied in a variety of diverse areas of sciences and prove to be productive and innovative. In fact, many researchers have shown that this theory provides the most natural, direct, simple, unified, and efficient framework for a general treatment of a wide class of unrelated linear and nonlinear problems.
Variational inclusion is an important generalization of variational inequality, which has been studied extensively by many authors (see, e.g., [2–14] and the references therein). In 2001, Huang and Fang [15] introduced the concept of a generalized  -accretive mapping, which is a generalization of an
-accretive mapping, which is a generalization of an  -accretive mapping, and gave the definition of the resolvent operator for the generalized
-accretive mapping, and gave the definition of the resolvent operator for the generalized  -accretive mapping in Banach spaces. Recently, Huang et al. [6, 7], Huang [8], Jin and Liu [9] and Lan et al. [11] introduced and studied some new classes of nonlinear variational inclusions involving generalized
-accretive mapping in Banach spaces. Recently, Huang et al. [6, 7], Huang [8], Jin and Liu [9] and Lan et al. [11] introduced and studied some new classes of nonlinear variational inclusions involving generalized  -accretive mappings in Banach spaces. By using the resolvent operator technique in [6], they constructed some new iterative algorithms for solving the nonlinear variational inclusions involving generalized
-accretive mappings in Banach spaces. By using the resolvent operator technique in [6], they constructed some new iterative algorithms for solving the nonlinear variational inclusions involving generalized  -accretive mappings. Further, they also proved the existence of solutions for nonlinear variational inclusions involving generalized
-accretive mappings. Further, they also proved the existence of solutions for nonlinear variational inclusions involving generalized  -accretive mappings and convergence of sequences generated by the algorithms.
-accretive mappings and convergence of sequences generated by the algorithms.
On the other hand, It is well known that the study of the random equations involving the random operators in view of their need in dealing with probabilistic models in applied sciences is very important. Motivated and inspired by the recent research works in these fascinating areas, the random variational inequality problems, random quasi-variational inequality problems, random variational inclusion problems and random quasi-complementarity problems have been introduced and studied by Ahmad and Bazán [16], Chang [17], Chang and Huang [18], Cho et al. [19], Ganguly and Wadhwa [20], Huang [21], Huang and Cho [22], Huang et al. [23], and Noor and Elsanousi [24].
Inspired and motivated by recent works in these fields (see [3, 11, 12, 16, 25–28]), in this paper, we introduce and study a new class of general nonlinear random multivalued operator equations involving generalized  -accretive mappings in Banach spaces. By using the Chang's lemma and the resolvent operator technique for generalized
-accretive mappings in Banach spaces. By using the Chang's lemma and the resolvent operator technique for generalized  -accretive mapping due to Huang and Fang [15], we also prove the existence theorems of the solution and convergence theorems of the generalized random iterative procedures with errors for this nonlinear random multivalued operator equations in
-accretive mapping due to Huang and Fang [15], we also prove the existence theorems of the solution and convergence theorems of the generalized random iterative procedures with errors for this nonlinear random multivalued operator equations in  -uniformly smooth Banach spaces. The results presented in this paper improve and generalize some known corresponding results in literature.
-uniformly smooth Banach spaces. The results presented in this paper improve and generalize some known corresponding results in literature.
Throughout this paper, we suppose that  is a complete
is a complete  -finite measure space and
-finite measure space and  is a separable real Banach space endowed with dual space
is a separable real Banach space endowed with dual space  , the norm
, the norm  and the dual pair
and the dual pair  between
between  and
and  . We denote by
. We denote by  the class of Borel
the class of Borel  -fields in
-fields in  . Let
. Let  and
and  denote the family of all the nonempty subsets of
denote the family of all the nonempty subsets of  , the family of all the nonempty bounded closed sets of
, the family of all the nonempty bounded closed sets of  , respectively. The generalized duality mapping
, respectively. The generalized duality mapping  is defined by
is defined by

for all  , where
, where  is a constant. In particular,
is a constant. In particular,  is the usual normalized duality mapping. It is well known that, in general,
is the usual normalized duality mapping. It is well known that, in general,  for all
for all  and
and  is single-valued if
is single-valued if  is strictly convex (see, e.g., [28]). If
is strictly convex (see, e.g., [28]). If  is a Hilbert space, then
is a Hilbert space, then  becomes the identity mapping of
becomes the identity mapping of  . In what follows we will denote the single-valued generalized duality mapping by
. In what follows we will denote the single-valued generalized duality mapping by  .
.
Suppose that  is a random multivalued operator such that for each fixed
is a random multivalued operator such that for each fixed  and
and  ,
,  is a generalized
is a generalized  -accretive mapping and
-accretive mapping and  . Let
. Let  ,
,  and
and  be single-valued operators, and let
be single-valued operators, and let  be three multivalued operators.
be three multivalued operators.
Now, we consider the following problem.
Find  such that
such that  ,
,  and
and

for all  and
and  . The problem (1.2) is called the general nonlinear random equation with multivalued operator involving generalized
. The problem (1.2) is called the general nonlinear random equation with multivalued operator involving generalized  -accretive mapping in Banach spaces.
-accretive mapping in Banach spaces.
Some special cases of the problem (1.2) are as follows.
-
(1)
If
 is a single-valued operator,
is a single-valued operator,  , the identity mapping and
, the identity mapping and 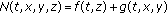 for all
for all 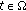 and
and  , then problem (1.2) is equivalent to finding
, then problem (1.2) is equivalent to finding 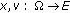 such that
such that 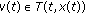 and
and

for all  and
and  . The determinate form of the problem (1.3) was considered and studied by Agarwal et al. [2] when
. The determinate form of the problem (1.3) was considered and studied by Agarwal et al. [2] when  .
.
-
(2)
If
 for all
for all 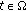 ,
, 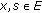 and, for all
and, for all 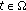 ,
, 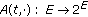 is a generalized
is a generalized 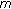 -accretive mapping, then the problem (1.2) reduces to the following generalized nonlinear random multivalued operator equation involving generalized
-accretive mapping, then the problem (1.2) reduces to the following generalized nonlinear random multivalued operator equation involving generalized 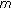 -accretive mapping in Banach spaces.
-accretive mapping in Banach spaces.
Find  such that
such that  and
and

for all  and
and  .
.
-
(3)
If
 is a Hilbert space and
is a Hilbert space and 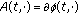 for all
for all 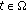 , where
, where 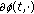 denotes the subdifferential of a lower semicontinuous and
denotes the subdifferential of a lower semicontinuous and 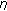 -subdifferetiable function
-subdifferetiable function 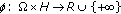 , then the problem (1.4) becomes the following problem.
, then the problem (1.4) becomes the following problem.
Find  such that
such that  and
and

for all  ,
,  and
and  , which is called the generalized nonlinear random variational inclusions for random multivalued operators in Hilbert spaces. The determinate form of the problem (1.5) was studied by Agarwal et al. [3] when
, which is called the generalized nonlinear random variational inclusions for random multivalued operators in Hilbert spaces. The determinate form of the problem (1.5) was studied by Agarwal et al. [3] when  for all
for all  , where
, where  is a single-valued operator.
is a single-valued operator.
-
(4)
If
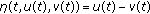 for all
for all 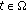 ,
,  , then the problem (1.5) reduces to the following nonlinear random variational inequalities.
, then the problem (1.5) reduces to the following nonlinear random variational inequalities.
Find  such that
such that  ,
,  and
and

for all  and
and  , whose determinate form is a generalization of the problem considered in [4, 5, 29].
, whose determinate form is a generalization of the problem considered in [4, 5, 29].
-
(5)
If, in the problem (1.6),
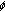 is the indictor function of a nonempty closed convex set
is the indictor function of a nonempty closed convex set 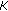 in
in 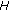 defined in the form
defined in the form  (17)
(17)
then (1.6) becomes the following problem.
Find  such that
such that  ,
,  and
and

for all  and
and  . The problem (1.8) has been studied by Cho et al. [19] when
. The problem (1.8) has been studied by Cho et al. [19] when  for all
for all  ,
,  .
.
Remark 1.1.
For appropriate and suitable choices of  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  and for the space
and for the space  , a number of known classes of random variational inequality, random quasi-variational inequality, random complementarity, and random quasi-complementarity problems were studied previously by many authors (see, e.g., [17–20, 22–24] and the references therein).
, a number of known classes of random variational inequality, random quasi-variational inequality, random complementarity, and random quasi-complementarity problems were studied previously by many authors (see, e.g., [17–20, 22–24] and the references therein).
In this paper, we will use the following definitions and lemmas.
Definition 1.2.
An operator  is said to be measurable if, for any
is said to be measurable if, for any  ,
,  .
.
Definition 1.3.
An operator  is called a random operator if for any
is called a random operator if for any  ,
,  is measurable. A random operator
is measurable. A random operator  is said to be continuous (resp., linear, bounded) if, for any
is said to be continuous (resp., linear, bounded) if, for any  , the operator
, the operator  is continuous (resp., linear, bounded).
is continuous (resp., linear, bounded).
Similarly, we can define a random operator  . We will write
. We will write  and
and  for all
for all  and
and  .
.
It is well known that a measurable operator is necessarily a random operator.
Definition 1.4.
A multivalued operator  is said to be measurable if, for any
is said to be measurable if, for any  ,
,  .
.
Definition 1.5.
An operator  is called a measurable selection of a multivalued measurable operator
is called a measurable selection of a multivalued measurable operator  if
if  is measurable and for any
is measurable and for any  ,
,  .
.
Definition 1.6.
A multivalued operator  is called a random multivalued operator if, for any
is called a random multivalued operator if, for any  ,
,  is measurable. A random multivalued operator
is measurable. A random multivalued operator  is said to be
is said to be  continuous if, for any
continuous if, for any  ,
,  is continuous in
is continuous in  , where
, where  is the Hausdorff metric on
is the Hausdorff metric on  defined as follows: for any given
defined as follows: for any given  ,
,

Definition 1.7.
A random operator  is said to be
is said to be
(a) strongly accretive if there exists
strongly accretive if there exists  such that
such that

for all  and
and  , where
, where  is a real-valued random variable;
is a real-valued random variable;
(b) Lipschitz continuous if there exists a real-valued random variable
Lipschitz continuous if there exists a real-valued random variable  such that
such that

for all  and
and  .
.
Definition 1.8.
Let  be a random operator. An operator
be a random operator. An operator  is said to be
is said to be
(a) strongly accretive with respect to
strongly accretive with respect to  in the first argument if there exists
in the first argument if there exists  such that
such that

for all  and
and  , where
, where  is a real-valued random variable;
is a real-valued random variable;
(b) Lipschitz continuous in the first argument if there exists a real-valued random variable
Lipschitz continuous in the first argument if there exists a real-valued random variable  such that
such that

for all  and
and  .
.
Similarly, we can define the Lipschitz continuity in the second argument and third argument of  .
.
Definition 1.9.
Let  be a random operator and
be a random operator and  be a random multivalued operator. Then
be a random multivalued operator. Then  is said to be
is said to be
(a) accretive if
accretive if

for all  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  , where
, where  ;
;
(b)strictly accretive if
accretive if

for all  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  and the equality holds if and only if
and the equality holds if and only if  for all
for all  ;
;
(c)strongly accretive if there exists a real-valued random variable
accretive if there exists a real-valued random variable  such that
such that

for all  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  ;
;
(d)generalized accretive if
accretive if  is
is  -accretive and
-accretive and  for all
for all  and (equivalently, for some)
and (equivalently, for some)  .
.
Remark 1.10.
If  is a Hilbert space, then (a)–(d) of Definition 1.9 reduce to the definition of
is a Hilbert space, then (a)–(d) of Definition 1.9 reduce to the definition of  -monotonicity, strict
-monotonicity, strict  -monotonicity, strong
-monotonicity, strong  -monotonicity, and maximal
-monotonicity, and maximal  -monotonicity, respectively; if
-monotonicity, respectively; if  is uniformly smooth and
is uniformly smooth and  , then (a)–(d) of Definition 1.9reduces to the definitions of accretive, strictly accretive, strongly accretive, and
, then (a)–(d) of Definition 1.9reduces to the definitions of accretive, strictly accretive, strongly accretive, and  -accretive operators in uniformly smooth Banach spaces, respectively.
-accretive operators in uniformly smooth Banach spaces, respectively.
Definition 1.11.
The operator  is said to be
is said to be
(a)monotone if

for all  and
and  ;
;
(b)strictly monotone if

for all  and
and  and the equality holds if and only if
and the equality holds if and only if  for all
for all  ;
;
(c) strongly monotone if there exists a measurable function
strongly monotone if there exists a measurable function  such that
such that

for all  and
and  ;
;
(d) Lipschitz continuous if there exists a real-valued random variable
Lipschitz continuous if there exists a real-valued random variable  such that
such that

for all  and
and  .
.
Definition 1.12.
A multivalued measurable operator  is said to be
is said to be  Lipschitz continuous if there exists a measurable function
Lipschitz continuous if there exists a measurable function  such that, for any
such that, for any  ,
,

for all  .
.
The modules of smoothness of  is the function
is the function  defined by
defined by

A Banach space  is called uniformly smooth if
is called uniformly smooth if  and
and  is called
is called  -uniformly smooth if there exists a constant
-uniformly smooth if there exists a constant  such that
such that  , where
, where  is a real number.
is a real number.
It is well known that Hilbert spaces,  (or
(or  ) spaces,
) spaces,  and the Sobolev spaces
and the Sobolev spaces  , are all
, are all  -uniformly smooth.
-uniformly smooth.
In the study of characteristic inequalities in  -uniformly smooth Banach spaces, Xu [30] proved the following result.
-uniformly smooth Banach spaces, Xu [30] proved the following result.
Lemma 1.13.
Let  be a given real number and let
be a given real number and let  be a real uniformly smooth Banach space. Then
be a real uniformly smooth Banach space. Then  is
is  -uniformly smooth if and only if there exists a constant
-uniformly smooth if and only if there exists a constant  such that, for all
such that, for all  and
and  , the following inequality holds:
, the following inequality holds:

Definition 1.14.
Let  be a generalized
be a generalized  -accretive mapping. Then the resolvent operator
-accretive mapping. Then the resolvent operator for
for  is defined as follows:
is defined as follows:

for all  and
and  , where
, where  is a measurable function and
is a measurable function and  is a strictly monotone mapping.
is a strictly monotone mapping.
From Huang et al. [6, 15], we can obtain the following lemma.
Lemma 1.15.
Let  be
be  -strongly monotone and
-strongly monotone and  -Lipschitz continuous. Let
-Lipschitz continuous. Let  be a generalized
be a generalized  -accretive mapping. Then the resolvent operator
-accretive mapping. Then the resolvent operator  for
for  is Lipschitz continuous with constant
is Lipschitz continuous with constant  , that is,
, that is,

for all  and
and  .
.
2. Random Iterative Algorithms
In this section, we suggest and analyze a new class of iterative methods and construct some new random iterative algorithms with errors for solving the problems (1.2)–(1.4), respectively.
Lemma 2.1 ([31]).
Let  be an
be an  -continuous random multivalued operator. Then, for any measurable operator
-continuous random multivalued operator. Then, for any measurable operator  , the multivalued operator
, the multivalued operator  is measurable.
is measurable.
Lemma 2.2 ([31]).
Let  be two measurable multivalued operators, let
be two measurable multivalued operators, let  be a constant, and let
be a constant, and let  be a measurable selection of
be a measurable selection of  . Then there exists a measurable selection
. Then there exists a measurable selection  of
of  such that, for any
such that, for any  ,
,

Lemma 2.3.
Measurable operators  are a solution of the problem (1.2) if and only if
are a solution of the problem (1.2) if and only if

where  and
and  is a real-valued random variable.
is a real-valued random variable.
Proof.
The proof directly follows from the definition of  and so it is omitted.
and so it is omitted.
Based on Lemma 2.3, we can develop a new iterative algorithm for solving the general nonlinear random equation (1.2) as follows.
Algorithm 2.4.
Let  be a random multivalued operator such that for each fixed
be a random multivalued operator such that for each fixed  and
and  ,
,  is a generalized
is a generalized  -accretive mapping, and
-accretive mapping, and  . Let
. Let  ,
,  and
and  be single-valued operators, and let
be single-valued operators, and let be three multivalued operators, and let
be three multivalued operators, and let  be a measurable step size function. Then, by Lemma 2.1 and Himmelberg [32], it is known that, for given
be a measurable step size function. Then, by Lemma 2.1 and Himmelberg [32], it is known that, for given  , the multivalued operators
, the multivalued operators  and
and  are measurable and there exist measurable selections
are measurable and there exist measurable selections  and
and  . Set
. Set

where  and
and  are the same as in Lemma 2.3 and
are the same as in Lemma 2.3 and  is a measurable function. Then it is easy to know that
is a measurable function. Then it is easy to know that  is measurable. Since
is measurable. Since  and
and  , by Lemma 2.2, there exist measurable selections
, by Lemma 2.2, there exist measurable selections  and
and  such that, for all
such that, for all  ,
,

By induction, one can define sequences  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  inductively satisfying
inductively satisfying

where  is an error to take into account a possible inexact computation of the resolvent operator point, which satisfies the following conditions:
is an error to take into account a possible inexact computation of the resolvent operator point, which satisfies the following conditions:

for all  .
.
From Algorithm 2.4, we can get the following algorithms.
Algorithm 2.5.
Suppose that  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  are the same as in Algorithm 2.4. Let
are the same as in Algorithm 2.4. Let  be a random single-valued operator,
be a random single-valued operator,  and
and  for all
for all  and
and  . Then, for given measurable
. Then, for given measurable  , one has
, one has

where  is the same as in Algorithm 2.4.
is the same as in Algorithm 2.4.
Algorithm 2.6.
Let  be a random multivalued operator such that for each fixed
be a random multivalued operator such that for each fixed  ,
,  is a generalized
is a generalized  -accretive mapping, and
-accretive mapping, and  . If
. If  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  are the same as in Algorithm 2.4, then, for given measurable
are the same as in Algorithm 2.4, then, for given measurable  , we have
, we have

where  is the same as in Algorithm 2.4.
is the same as in Algorithm 2.4.
Remark 2.7.
Algorithms 2.4–2.6 include several known algorithms of [2, 4–9, 12, 17–23, 25, 26, 29] as special cases.
3. Existence and Convergence Theorems
In this section, we will prove the convergence of the iterative sequences generated by the algorithms in Banach spaces.
Theorem 3.1.
Suppose that  is a
is a  -uniformly smooth and separable real Banach space,
-uniformly smooth and separable real Banach space,  is
is  -strongly accretive and
-strongly accretive and  -Lipschitz continuous, and
-Lipschitz continuous, and  is a random multivalued operator such that for each fixed
is a random multivalued operator such that for each fixed  and
and  ,
,  is a generalized
is a generalized  -accretive mapping and
-accretive mapping and  . Let
. Let  be
be  -strongly monotone and
-strongly monotone and  -Lipschitz continuous, and let
-Lipschitz continuous, and let  be a
be a  -Lipschitz continuous random operator, and let
-Lipschitz continuous random operator, and let  be
be  -strongly accretive with respect to
-strongly accretive with respect to  and
and  -Lipschitz continuous in the first argument, and
-Lipschitz continuous in the first argument, and  -Lipschitz continuous in the second argument,
-Lipschitz continuous in the second argument,  -Lipschitz continuous in the third argument, respectively. Let multivalued operators
-Lipschitz continuous in the third argument, respectively. Let multivalued operators  be
be  -
- -Lipschitz continuous,
-Lipschitz continuous,  -
- -Lipschitz continuous,
-Lipschitz continuous,  -
- -Lipschitz continuous, respectively. If there exist real-valued random variables
-Lipschitz continuous, respectively. If there exist real-valued random variables  and
and  such that, for any
such that, for any  ,
,  ,
,


where  is the same as in Lemma 1.13, then, for any
is the same as in Lemma 1.13, then, for any  , there exist
, there exist  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  such that
such that  is a solution of the problem (1.2) and
is a solution of the problem (1.2) and

as  , where
, where  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  are iterative sequences generated by Algorithm 2.4.
are iterative sequences generated by Algorithm 2.4.
Proof.
It follows from (2.5), Lemma 1.15 and (3.1) that

Since  is strongly accretive and Lipschitz continuous,
is strongly accretive and Lipschitz continuous,

that is,

where  is the same as in Lemma 1.13. Also from the strongly accretivity of
is the same as in Lemma 1.13. Also from the strongly accretivity of  with respect to
with respect to  and the Lipschitz continuity of
and the Lipschitz continuity of  in the first argument, we have
in the first argument, we have

By Lipschitz continuity of  in the second and third argument, and
in the second and third argument, and  -Lipschitz continuity of
-Lipschitz continuity of  , we obtain
, we obtain



Using (3.6)–(3.10) in (3.4), we have, for all 

where

Let

Then  ,
,  as
as  . From the condition (3.2), we know that
. From the condition (3.2), we know that  for all
for all  and so there exists a positive measurable function
and so there exists a positive measurable function  such that
such that  for all
for all  and
and  . Therefore, for all
. Therefore, for all  , by (3.11), we now know that, for all
, by (3.11), we now know that, for all  ,
,

which implies that, for any  ,
,

Since  and
and  for all
for all  , it follows from (2.6) and (3.15) that
, it follows from (2.6) and (3.15) that  and so
and so  is a Cauchy sequence. Setting
is a Cauchy sequence. Setting  as
as  for all
for all  . From (3.8)–(3.10), we know that
. From (3.8)–(3.10), we know that  ,
,  ,
,  are also Cauchy sequences. Hence there exist
are also Cauchy sequences. Hence there exist  such that
such that  ,
,  ,
,  as
as  .
.
Now, we show that  . In fact, we have
. In fact, we have

This implies that  . Similarly, we have
. Similarly, we have  and
and  . Therefore, from (2.5), (2.6) and the continuity of
. Therefore, from (2.5), (2.6) and the continuity of  ,
,  and
and  , we have
, we have

By Lemma 2.3, now we know that  is a solution of the problem (1.2). This completes the proof.
is a solution of the problem (1.2). This completes the proof.
Remark 3.2.
If  is a 2-uniformly smooth Banach space and there exists a measurable function
is a 2-uniformly smooth Banach space and there exists a measurable function  such that
such that

then (3.2) holds. We note that Hilbert spaces and  (or
(or  ) spaces,
) spaces,  , are 2-uniformly smooth.
, are 2-uniformly smooth.
From Theorem 3.1, we can get the following theorems.
Theorem 3.3.
Let  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  be the same as in Theorem 3.1. Assume that
be the same as in Theorem 3.1. Assume that  is a random multivalued operator such that, for each fixed
is a random multivalued operator such that, for each fixed  and
and  ,
,  is a generalized
is a generalized  -accretive mapping. Let
-accretive mapping. Let  be
be  -Lipschitz continuous, let
-Lipschitz continuous, let  be a
be a  -Lipschitz continuous random operator, let
-Lipschitz continuous random operator, let  be
be  -Lipschitz continuous, and let
-Lipschitz continuous, and let  be
be  -strongly accretive with respect to
-strongly accretive with respect to  and
and  -Lipschitz continuous in the first argument and
-Lipschitz continuous in the first argument and  -Lipschitz continuous in the second argument, respectively. If there exist real-valued random variables
-Lipschitz continuous in the second argument, respectively. If there exist real-valued random variables  and
and  such that (3.1) holds and
such that (3.1) holds and

for all  , where
, where  is the same as in Lemma 1.13, then, for any
is the same as in Lemma 1.13, then, for any  , the iterative sequences
, the iterative sequences  ,
,  and
and  defined by Algorithm 2.5 converge strongly to the solution
defined by Algorithm 2.5 converge strongly to the solution  of the problem (1.3).
of the problem (1.3).
Theorem 3.4.
Suppose that  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  are the same as in Algorithm 2.4. Let
are the same as in Algorithm 2.4. Let  be a random multivalued operator such that, for each fixed
be a random multivalued operator such that, for each fixed  ,
,  is a generalized
is a generalized  -accretive mapping and
-accretive mapping and  . If there exists a real-valued random variable
. If there exists a real-valued random variable  such that, for any
such that, for any  ,
,

where  is the same as in Lemma 1.13, then, for any
is the same as in Lemma 1.13, then, for any  , the iterative sequences
, the iterative sequences  ,
,  and
and  defined by Algorithm 2.6 converge strongly to the solution
defined by Algorithm 2.6 converge strongly to the solution  of the problem (1.4).
of the problem (1.4).
Remark 3.5.
For an appropriate choice of the mappings  and the space
and the space  , Theorems 3.1–3.4 include many known results of generalized variational inclusions as special cases (see [2, 4–9, 12, 17–23, 25, 26, 29] and the references therein).
, Theorems 3.1–3.4 include many known results of generalized variational inclusions as special cases (see [2, 4–9, 12, 17–23, 25, 26, 29] and the references therein).
References
Hartman P, Stampacchia G: On some non-linear elliptic differential-functional equations. Acta Mathematica 1966,115(1):271–310. 10.1007/BF02392210
Agarwal RP, Cho YJ, Huang N-J: Generalized nonlinear variational inclusions involving maximal -monotone mappings. In Nonlinear Analysis and Applications: to V. Lakshmikantham on His 80th Birthday. Vol. 1, 2. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands; 2003:59–73.
Agarwal RP, Khan MF, O'Regan D, Salahuddin : On generalized multivalued nonlinear variational-like inclusions with fuzzy mappings. Advances in Nonlinear Variational Inequalities 2005,8(1):41–55.
Ding XP: Generalized quasi-variational-like inclusions with nonconvex functionals. Applied Mathematics and Computation 2001,122(3):267–282. 10.1016/S0096-3003(00)00027-8
Huang N-J: Generalized nonlinear variational inclusions with noncompact valued mappings. Applied Mathematics Letters 1996,9(3):25–29. 10.1016/0893-9659(96)00026-2
Huang N-J, Fang Y-P: A new class of general variational inclusions involving maximal -monotone mappings. Publicationes Mathematicae Debrecen 2003,62(1–2):83–98.
Huang NJ, Fang YP, Deng CX: Nonlinear variational inclusions involving generalized -accretive mappings. Proceedings of the 9th Bellman Continuum International Workshop on Uncertain Systems and Soft Computing, July 2002, Beijing, China 323–327.
Huang N-J: Nonlinear implicit quasi-variational inclusions involving generalized -accretive mappings. Archives of Inequalities and Applications 2004,2(4):413–425.
Jin M-M, Liu Q-K: Nonlinear quasi-variational inclusions involving generalized -accretive mappings. Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications 2004,9(3):485–494.
Lan H-Y, Kim JK, Huang NJ: On the generalized nonlinear quasi-variational inclusions involving non-monotone set-valued mappings. Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications 2004,9(3):451–465.
Lan H-Y, Liu Q-K, Li J: Iterative approximation for a system of nonlinear variational inclusions involving generalized -accretive mappings. Nonlinear Analysis Forum 2004,9(1):33–42.
Liu L-W, Li Y-Q: On generalized set-valued variational inclusions. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2001,261(1):231–240. 10.1006/jmaa.2001.7493
Verma RU, Khan MF, Salahuddin : Generalized setvalued nonlinear mixed quasivariational-like inclusions with fuzzy mappings. Advances in Nonlinear Variational Inequalities 2005,8(2):11–37.
Lan H-Y, He Z-Q, Li J: Generalized nonlinear fuzzy quasi-variational-like inclusions involving maximal -monotone mappings. Nonlinear Analysis Forum 2003,8(1):43–54.
Huang NJ, Fang YP: Generalized -accretive mappings in Banach spaces. Journal of Sichuan University 2001,38(4):591–592.
Ahmad R, Bazán FF: An iterative algorithm for random generalized nonlinear mixed variational inclusions for random fuzzy mappings. Applied Mathematics and Computation 2005,167(2):1400–1411. 10.1016/j.amc.2004.08.025
Chang SS: Variational Inequality and Complementarity Problem Theory with Applications. Shanghai Scientific and Technological Literature, Shanghai, China; 1991.
Chang SS, Huang NJ: Generalized random multivalued quasi-complementarity problems. Indian Journal of Mathematics 1993,35(3):305–320.
Cho YJ, Huang NJ, Kang SM: Random generalized set-valued strongly nonlinear implicit quasi-variational inequalities. Journal of Inequalities and Applications 2000,5(5):515–531. 10.1155/S1025583400000308
Ganguly A, Wadhwa K: On random variational inequalities. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 1997,206(1):315–321. 10.1006/jmaa.1997.5194
Huang N-J: Random generalized nonlinear variational inclusions for random fuzzy mappings. Fuzzy Sets and Systems 1999,105(3):437–444. 10.1016/S0165-0114(97)00222-4
Huang N-J, Cho YJ: Random completely generalized set-valued implicit quasi-variational inequalities. Positivity 1999,3(3):201–213. 10.1023/A:1009784323320
Huang N-J, Long X, Cho YJ: Random completely generalized nonlinear variational inclusions with non-compact valued random mappings. Bulletin of the Korean Mathematical Society 1997,34(4):603–615.
Noor MA, Elsanousi SA: Iterative algorithms for random variational inequalities. Panamerican Mathematical Journal 1993,3(1):39–50.
Cho YJ, Shim SH, Huang NJ, Kang SM: Generalized strongly nonlinear implicit quasi-variational inequalities for fuzzy mappings. In Set Valued Mappings with Applications in Nonlinear Analysis, Series in Mathematical Analysis and Applications. Volume 4. Taylor & Francis, London, UK; 2002:63–77.
Cho YJ, Lan H-Y: Generalized nonlinear random -accretive equations with random relaxed cocoercive mappings in Banach spaces. Computers & Mathematics with Applications 2008,55(9):2173–2182. 10.1016/j.camwa.2007.09.002
Lan H-Y, Huang N-J, Cho YJ: A new method for nonlinear variational inequalities with multi-valued mappings. Archives of Inequalities and Applications 2004,2(1):73–84.
Verma RU: A class of projection-contraction methods applied to monotone variational inequalities. Applied Mathematics Letters 2000,13(8):55–62. 10.1016/S0893-9659(00)00096-3
Hassouni A, Moudafi A: A perturbed algorithm for variational inclusions. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 1994,185(3):706–712. 10.1006/jmaa.1994.1277
Xu HK: Inequalities in Banach spaces with applications. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications 1991,16(12):1127–1138. 10.1016/0362-546X(91)90200-K
Chang SS: Fixed Point Theory with Applications. Chongqing Publishing, Chongqing, China; 1984.
Himmelberg CJ: Measurable relations. Fundamenta Mathematicae 1975, 87: 53–72.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Scientific Research Fund of Sichuan Provincial Education Department (2006A106) and the Sichuan Youth Science and Technology Foundation (08ZQ026-008). This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (KRF-2008-313-C00050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, HY., Cho, Y.J. & Xie, W. General Nonlinear Random Equations with Random Multivalued Operator in Banach Spaces. J Inequal Appl 2009, 865093 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/865093
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/865093
 is a single-valued operator,
is a single-valued operator,  , the identity mapping and
, the identity mapping and 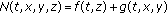 for all
for all 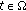 and
and  , then problem (1.2) is equivalent to finding
, then problem (1.2) is equivalent to finding 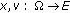 such that
such that 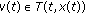 and
and for all
for all 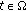 ,
, 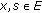 and, for all
and, for all 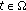 ,
, 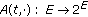 is a generalized
is a generalized 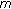 -accretive mapping, then the problem (1.2) reduces to the following generalized nonlinear random multivalued operator equation involving generalized
-accretive mapping, then the problem (1.2) reduces to the following generalized nonlinear random multivalued operator equation involving generalized 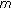 -accretive mapping in Banach spaces.
-accretive mapping in Banach spaces. is a Hilbert space and
is a Hilbert space and 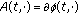 for all
for all 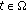 , where
, where 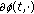 denotes the subdifferential of a lower semicontinuous and
denotes the subdifferential of a lower semicontinuous and 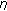 -subdifferetiable function
-subdifferetiable function 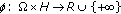 , then the problem (1.4) becomes the following problem.
, then the problem (1.4) becomes the following problem.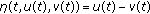 for all
for all 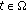 ,
,  , then the problem (1.5) reduces to the following nonlinear random variational inequalities.
, then the problem (1.5) reduces to the following nonlinear random variational inequalities.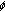 is the indictor function of a nonempty closed convex set
is the indictor function of a nonempty closed convex set 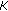 in
in 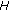 defined in the form
defined in the form 